You’ve probably heard of people taking out loans when they need to realize a big purchase. They go to a bank, and it lends them money which has to be repaid with interest. Those interests are how the bank makes money. But, what if you were the one receiving interest? Yes, there are crypto projects out there that allow you to loan your cryptocurrencies to receive interest. This is known as crypto lending.
What is DeFi or decentralized finance?
Since the beginning of 2020, the entire cryptosphere has been buzzing about decentralized finance or DeFi. However, this ever-evolving ecosystem remains a mystery to many newbies just entering the crypto world. Decentralized finance, commonly referred to as DeFi, is a segment of the crypto ecosystem that aims to transpose traditional financial services onto the blockchain.
Initially, Bitcoin (BTC) revolutionized the monetary system by offering a decentralized currency, in other words, a currency without any centralized control. As a result, Bitcoin provides an alternative currency outside of the rule of banks. Meanwhile, the decentralized finance ecosystem is building on the foundations laid out by Bitcoin to offer a panel of decentralized financial services.
In the early days of the DeFi ecosystem, all the services relied on the Ethereum network because it pioneered and democratized smart contracts. As a reminder, smart contracts are programs that automatically execute actions according to a set of conditions. Now, decentralized finance is a burgeoning ecosystem that spans many networks.
Crypto lending, the origin of the decentralized finance ecosystem
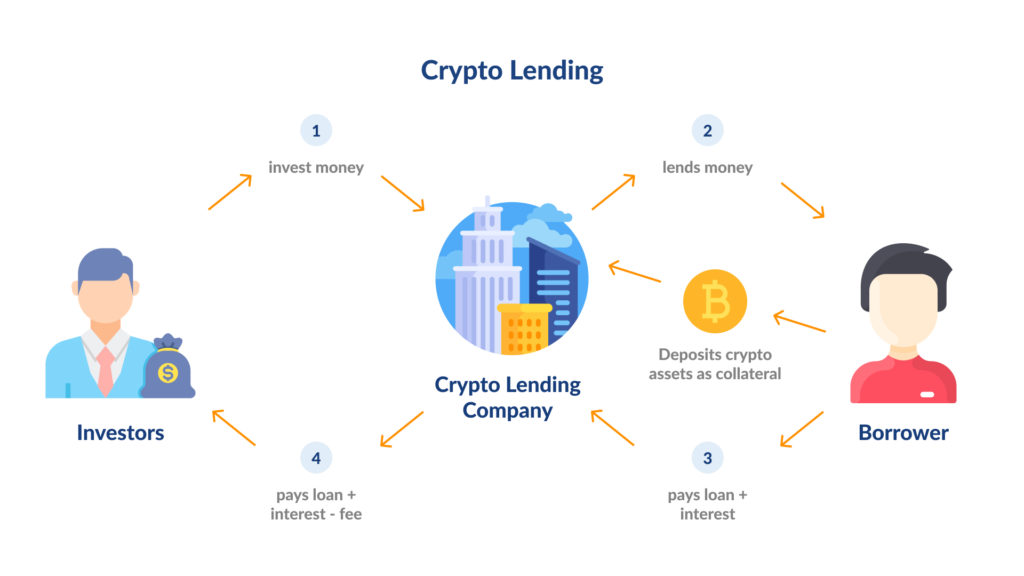
In the cryptosphere, lending refers to decentralized finance activities allowing users to lend their crypto assets to borrowers to earn a yield. On one side, you have borrowers who can use their crypto-assets as collateral to obtain a loan labeled in crypto or stablecoin. On the other side, you have lenders who provide the assets for the loans and receive interest during the deposit span.

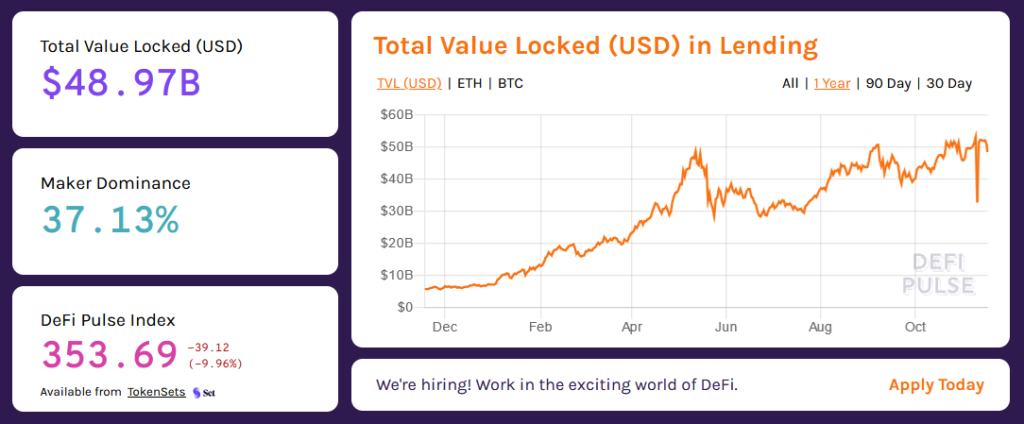
The total value committed to decentralized lending grew exponentially during the 2021 bull run. On the one hand, this is due to the price increase of most assets. On the other hand, the juicy returns offered by lending platforms drove the rise in value committed to lending. The total value of the crypto assets committed to the DeFi protocols is the Total Value Locked or TVL.
Crypto-enthusiasts often hold their assets for extended periods of time, waiting for the price to go to the moon. But, while you hold, your capital isn’t working for you, and you’re not making actual profits. The fact that most crypto investors hold their assets for several weeks or months is one of the reasons for the success of crypto lending.
While holding your favorite crypto asset, you can deposit it on lending platforms and earn interest until you choose to sell them for a profit. This is a win-win situation where lenders earn rewards while providing liquidity to the market. In 2021, the TVL of the lending ecosystem increased fivefold and reached a peak of $53 billion.
MakerDAO, the precursor of DeFi loans
MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that built the first-ever DeFi protocol. Based on the Ethereum network, it allows lending and borrowing of cryptocurrencies without any intermediaries. MakerDAO’s protocol is a series of smart contracts designed to handle all the lending operations. The platform relies on its two native currencies, the DAI and the MKR. The DAI is a stablecoin given to users who deposit collateral in the smart contracts, while MKR is used to regulate the value of the loans.
The innovation brought by this DAO is tremendous; it allows anyone with ETH and a MetaMask wallet to obtain loans by depositing Ether (ETH) on MakerDAO’s platform.
How do crypto loans work?
The backbones of the lending ecosystem are smart contracts and liquidity pools. Smart contracts are pieces of code that run permanently on a given blockchain without the need for human intervention. In lending protocols, smart contracts manage the pools used to deposit and distribute the funds.
First, a lender interacts with the contract to deposit funds. When a borrower wants to subscribe to a loan, he has to deposit collateral in the smart contract that’s at least as valuable as the loans he takes. Then the contract distributes the assets amongst the borrowers according to the contract rules and distributes interest to the lenders.
The collateral ratio depends on the protocol you use. In general, you have to deposit a value equivalent to the amount of the loan. If you want to borrow 100 USDT, you have to deposit $100 worth of crypto on the smart contract. However, some platforms like MakerDAO impose a 150% collateral ratio to ensure a healthier lending system.
Last but not least, crypto lending isn’t a risk-less activity for borrowers. Indeed, when the collateral’s value starts to diminish, the smart contract can liquidate the assets to reimburse the loans. For instance, MakerDAO has a minimum collateral requirement of 150%. When the collateral’s value goes below 120% of the value of the loans, the smart contract will sell the assets because the rules of the contract stipulate that the lenders in the pools can’t lose money. In the end, the borrowers support the loss, not the lenders.
The types of lending platforms
Since MakerDAO launched the first lending platform in 2018, this segment of the crypto ecosystem has experienced tremendous growth. You can now access a wide range of crypto lending services with their respective pros and cons.

Decentralized non-custodial crypto lending platforms
Despite being the first-ever DeFi application, MakerDAO is only in charge of providing the infrastructure supporting the DAI stablecoin. Basically, MakerDAO operates the back-end of the lending infrastructure while other projects handle the user-facing interface. In MakerDAO’s case, the most commonly used application is Oasis.app.
The advantage of using a decentralized non-custodial lending platform is that anyone can access it at any time and without KYC (a know-your-customer procedure). With the exception of Maker, whose decentralized governance system determines interest rates, these platforms offer interest rates that vary based on the supply and demand for an asset. This cryptographic regulation of interest rates can lead to significant spikes when an asset is in high demand.
Centralized crypto lending platforms
On the other end of the crypto lending spectrum, you have centralized platforms like BlockFi or Celsius. Centralized lending platforms are more like traditional fintech that work with cryptocurrencies. These platforms tend to offer fixed interest rates. But, to access them, this time, you will have to go through the KYC procedure to open an account. For instance, the BlockFi interest account offers a 9.5% annual yield on several stablecoins and up to 5% yields on cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ether (ETH), Litecoin (LTC).

Even if those centralized platforms are generally safer than DeFi protocols, the yield you can earn from them is always lower than those in the DeFi ecosystem. On BlockFi, the best return possible on a stablecoin is 9.5% over a year for a USDT deposit. In comparison, you can earn more than 19% on your stablecoin deposits by using Anchor decentralized lending protocol.
Lending and regulation
In essence, lending entities intend to transpose the traditional financial services on the blockchain to improve their efficiency and democratize access. But, in the world of traditional finance, those activities are highly regulated. Banks need a banking license to operate and are controlled by a wide range of governmental bodies. In contrast, general financial services companies need to register themselves with a regulator to offer their services to the public. With the continuous growth of the crypto lending ecosystem, regulators worldwide started to look closely at crypto lending services, and most of them do not comply with existing regulations.
In early September 2021, the Security and Exchanges Commission (SEC) sent a warning notice to Coinbase concerning its lending services. Coinbase intended to launch fixed rates lending services for its retail users. The Lend product planned to offer a 4% return on USDC deposits, but it didn’t sit well with the SEC. The regulator argued that the Lend product would represent an unregistered security offering. Coinbase attempted to defend itself but had to give in to the regulator. In the end, regulators are the Achille’s heels of centralized entities and can bend them to their will by threatening to shut them down if they don’t comply.
For the moment, DeFi lending services are relatively safe from the regulator’s pressure since a single legal entity does not operate them. Nevertheless, the DeFi ecosystem has piqued the curiosity of regulators around the world, who are looking for ways to regulate this sector. From the European Commission to the Financial Action Task Force, everyone is looking at DeFi!
Recent Comments